Climate Change
Climate Change has become a word which no longer needs a definition anymore. Unfortunately, we live in an era where we are first hand experiencing the effects of climate change. It has not only caused a shift in the Earth’s weather patterns and average temperatures but has also affected a lot of people and their communities. Increased levels of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxides, and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which have been generated since the industrialization, are leading to increased global warming.

Globally there is an increasing awareness regarding the perils of climate change. Under the aegis of the UNFCCC, nations have come together to institute a concerted plan of action under the Paris Agreement to contain the global temperature rise in this century under 2˚C, if not under 1.5˚C. However, in spite of the several actions planned, it is being realised that additional efforts need to be put in place to achieve the global target of 2˚C. One of the major areas that is being now targeted is the decarbonisation of the industrial sectors specifically Steel, Cement, Petrochemicals, and fertiliser, which essentially use fossil fuels as their raw material.
Among the above industries, steel accounts for nearly 50% of the carbon emissions. By 2050, the carbon intensity of steel production needs to be reduced by at least 70% globally, to be able to maintain the temperature rise within the 2˚C scenario. In India, the Ministry of Steel has committed a reduction of a specific emission of carbon dioxide to around 2.0tCO2/tcs by 2030 from 3.0t CO2/tcs in 2005 and transition towards a pathway to ‘Zero Carbon Steel’.
As India’s leading steel producer, JSW Steel, has taken the challenge to combat climate change by incorporating sustainability to its core operations and decision making. JSW Steel is committed to the reduction of a specific emission of carbon dioxide to around 1.95 tCO2/tcs by 2030.
To achieve this JSW has taken a pledge for -
1) Prevention of the causes of climate change
2) Mitigation and adaptation of the impacts of climate change
3) Building resilience to climate change
SDG Mapping of JSW Steel’s Initiatives & Projects
SDG 13: Climate Action
JSW Steel and its subsidiaries together account for ~23% of India’s steel production. As one of the premier players in the industry, we consider it our responsibility to proactively reflect on and manage the challenges arising out of climate change. JSW has integrated climate change scenarios in its risk management system to build resilience and strengthen adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters. Some of the major tasks undertaken by JSW Steel to manage its climate change-related risks and opportunities are,
Climate Action Group
Considering the rapid developments related to climate change viz. technology, regulations, taxation, investors’ growing expectations, disclosures, and so on, we have constituted a Climate Action Group (CAG) with cross-functional expertise encompassing R&D, strategy, operations, communications, etc. Facilitated by the Corporate Sustainability Team, including the Chief Sustainability Officer (CSO), the CAG operates as a central think-tank, to formulate and drive the climate change mitigation strategy and actions for JSW Steel towards a low carbon road ahead.
The primary responsibilities of the CAG are expected to be:

Conducting Scenario Analysis for Climate Change Risk Assessment
JSW Steel is currently conducting a detailed scenario-based climate change risk and opportunity assessment study to understand the long-term impacts of climate risks and opportunities on the company’s operations across India. The study encompasses an assessment of both physical and transition risks that JSW Steel’s operations are likely to face.
With regards to physical risks, JSW Steel is considering two scenarios – a Business-As-Usual scenario and an Optimistic scenario aligned with the Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) 8.5 and RCP4.5 scenarios respectively, as defined by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Detailed analysis of site-specific climate risks is being carried out involving the assessment of changes in key climatic parameters that are likely to impact JSW Steel’s operations, such as temperature, rainfall, water stress and sea level rise, under these scenarios.
As one of the leading producers of steel in India, it is important for JSW Steel to adopt technologies and low carbon pathways that are compatible with the goals of the Paris Agreement. This is why when it comes to the assessment of transition risks, JSW Steel is currently considering the use of the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Stated Policy Scenario (STEPS) and Sustainable Development Scenario (SDS) which take into account the 2oC limiting goal of the Paris Agreement. With these scenarios, JSW Steel is currently exploring the various policy, market, technology, and reputational risks and opportunities that are likely to associated with various climate-related elements such as upcoming climate-related regulations (e.g. EU CBAM), market trends (e.g. increased demand for low carbon steel) and a transition towards low carbon technologies (e.g. increased use of hydrogen as a fuel), amongst others.
While the aforementioned scenarios are being utilized to assess JSW Steel’s exposure to climate risks and opportunities, the process of assessment is currently ongoing and could witness the addition of scenarios to suit the business needs of the organization as and if it sees fit.
ESG Risk Management- Emerging Risks
| Name of the Emerging Risk | Natural disasters and extreme weather events | Biodiversity Loss |
| Description | As a result of climate change, there have been a surge in the extreme weather events resulting into natural disasters. Considering our value chain including our supplier base is spread across various geographies, there can be significant challenges to our value chain as well as operations. Any changes in weather conditions or other natural exigencies across the any geography can have a significant impact which are beyond the control of the Company. | Biodiversity loss poses a great threat to ecosystem balance. Our natural habitat is being exploited at an unprecedented rate leading endangered of species, habitat loss, alteration of landscape, and impact on wildlife. Some of these impacts are irreversible in nature. The Global Risk Report 2023 published by World Economic Forum has also identified biodiversity loss as one of the top 5 risks. |
| Impact | The world is already witnessing extreme weather events due to the effect of climate change, causing unpredictable natural disasters such as floods, extreme temperature, droughts among others. Considering nature of our operations, extensive supply chain and results of our assessments – irrespective of scenarios, climate-related risks such as extreme weather events are material for our operations and have the potential to adversely impact our business. An event of extreme weather events such as cyclones, floods, etc. can lead to disruptions in our operations as well as the supply chain to a larger extent. Any disruption in supply chain will directly lead to unavailability of raw material and/or other necessary equipment thereby, resulting in production losses, increased cost, loss of revenue, and higher prices or shortages for customers. Thus, leading to both direct as well as indirect physical risks. | Biodiversity loss can lead to ecosystem collapse. Considering the nature of the industry, we are prone to have a direct impact on the adjacent biodiversity. Any loss of biodiversity can lead to direct or indirect risks such as regulatory risks and risks due to community unrest, and reputational risks. These risks can lead to economic and financial losses to the company through operational disruptions, legal fines/ penalties, loss of consumers. Much of these risks arise from our upstream supply chain which involve sourcing of raw materials required for production. |
| Mitigating Actions | We closely monitor and forecast the probability of occurrence of such events through our established risk management framework. We have integrated sustainability risk into our organizational ERM. We carried out a scenario-based climate change risk assessment exercise for our Vijayanagar, Dolvi, and Salem operations to determine potential implications of climate risks on our business. Based on the scenario analysis, we identified that extreme rainfall and flooding may have medium- to long-term impact on our operations. In response to it, we have a business continuity and a disaster management plan in place, reviewed and approved by the Board. To make our BCP more robust, we plan regular training and awareness sessions across the plant locations. We also conduct periodic BCP testing to check its efficacy and improve it further based on the gaps observed during testing. We have also diversified our supplier base to make it more resilient. |
We recognize biodiversity as a core focus area. We are aligned to the National Biodiversity Targets and take a risk-based approach for making biodiversity a key decision-making consideration. We are also a Working Group (WG) and founding member of the India Business and Biodiversity Initiative (IBBI) Chapter of CII-CESD. As an effort to conserve biodiversity, we have developed biodiversity management plans, especially for our mining operations. We have taken up a Mangrove restoration project at Dolvi and planted more than a million saplings in the span of 4 years thereby bringing 340 hectares of land under forest cover which is estimated to have carbon capture, over a 25-year period, of approximately 185,000 tonnes. We are also committed to “No Net Loss” of biodiversity by 2030. |
Internal Carbon Price
JSW Steel has adopted a shadow internal carbon price of USD 20/tonne
Lobbying and Trade Associations
The purpose of our advocacy is to find common ground and act collaboratively with stakeholders. We work with industry, governments, civil society and consumers at a local, regional, national and international level. We have a robust process to assess and determine the importance of public policy issues.
The Board and the Sustainability Committee have stewardship over political lobbying activities, providing oversight on our approach and ensuring alignment with the Company’s interests and strategic priorities, in accordance with the applicable policies including Policy on Influencing Public and Regulatory Policy, Policy on Business Conduct, and Climate Change Policy.
Our direct lobbying efforts are aligned with our policies and strategic priorities and goals. We may engage in indirect lobbying through multiple industry organizations and think tanks at local, regional and global level, such as WBCSD, WSA, ISA, CII, FICCI, ASSOCHAM, etc. We believe in the power of collective action, especially on challenging topics that cannot be tackled alone, including many environmental and social issues. Our membership in any such organization does not imply that we agree with or endorse every position that these groups may take.
We work with the other members to ensure that lobbying, if any, conducted through trade organizations reflects our values and concerns. We engage in climate-related advocacy to encourage the reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and consequently, transition towards net zero through government policies and private sector leadership. Our lobbying efforts are aligned with the Paris Agreement, and include strong support for policies that will incentivize emission reductions.
We also take part in providing our alignment on topics such as Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Energy Transitions, Carbon Tax and Carbon pricing, Water and Waste Management, Sustainable Mining. In case of any misalignment, we ensure that we reserve our right to act as an individual company and transparently communicate our stand to the respective stakeholders.
We regularly review our involvement in industry and trade organizations to assess the relevance of our participation in line with our strategy, which is aligned with the Paris Agreement. The purpose of our advocacy is to find common ground and act collaboratively with stakeholders at all our operational locations.
Worldsteel Association Climate Action Member
JSW Steel has been recognized by the World Steel Association for fulfilling the commitment to participate in the Climate Action Program for CO2 emissions data collection for two consecutive years. In 2008, Climate Action was launched by Worldsteel with an aim to collect and report CO2 emissions data for both on site-level and company-level CO2 emissions in order to obtain a base level of emissions for the steel industry as a whole. This data collection program is at the core of the steel industry's global steel sectoral approach to climate change. More details can be found here
CDP
As the world takes steps towards building climate resilience, disclosure of the same provides the bedrock for ambitious action. CDP is one such global platform for climate related disclosures – actions & progress towards building a truly sustainable economy for people and planet. By reporting to CDP, JSW Group companies (JSW Steel, JSW Energy & JSW Cement) gain competitive advantage as it helps to identify and tackle growing risks and find new opportunities. While JSW Steel has been associated with CDP since a 2013, JSW Energy & JSW Cement started disclosing the data in the recent years. In terms of carbon footprint, JSW Steel has been rated ‘A’ by the CDP. This score pertains to the ‘Leadership’ band, and is the highest echelon one can reach in terms of CDP ratings - which acknowledges that the Company is implementing current best practices. This score is higher than the Global average of C, Asia regional average of C, and the Metal smelting, refining & forming sector average of C.
CII Working Group
JSW is the convener of the CII Working Group for Green House Gas (GHG) data collection from Industrial Processes and Product Use (IPPU) sectors for Iron & Steel and Cement.
Other key aspects of our climate change resilience building exercise
- JSW Steel and its subsidiaries together account for ~23% of India’s steel production. As one of the premier players in the industry, we consider it our responsibility to proactively consider and manage the challenges arising out of climate change.
- JSW Group is shifting its focus to increase the share of renewable/non-conventional energy consumption. JSW Energy is also looking at increasing the renewable energy in its production portfolio through solar & hydropower plants.
- The most recent initiative of JSW Group to improve the environment is the “Single Use Plastic Ban” across all JSW Group manufacturing locations. Through this JSW has successfully built awareness among its employees and their families on the negative impacts of plastic on our environment and promoted the use of alternative sustainable materials. JSW Steel also plans for plastic waste utilization in its coke oven & Electric Arc Furnace. For more details on all the projects taken up by JSW in the field of waste management please visit the Waste Framework.
- Through various initiatives of awareness improvement and building institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction, and early warning, JSW is contributing to Goal 3 of SDG 13.
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Climate change is associated with the exploitation of natural resources and JSW has taken upon itself to achieve sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. Details of all the projects taken up by JSW in the field of resource management can be found in Resource Framework.
- JSW Steel also incorporates social and environmental considerations while developing products. Key examples include:
- Speciality steel that is used to manufacture energy-efficient motors
- Steel structures that are used to install solar panels
- Products for the agricultural market that have helped farmers to prevent spoilage of food grains and other crop yields
- Products for the automobile industry that enable import substitution, leading to local employment generation and savings of foreign exchange
- Given the fact that steel maintains an average of 86% recyclability, a substantial quantity of steel demand can be met using converted steel scrap. This ability of steel to be recycled again and again makes it a perfect material for circular economy.
Circular Economy
- A circular economy is an economic system of closed loops in which raw materials, components, and products lose their value as little as possible, renewable energy sources are used and systems thinking is at the core.
- As a permanent material, steel is fundamental to achieving a circular economy through the 4 Rs – Reduce, Reuse, Remanufacture & Recycle.
- Reduce – To promote circular economy of steel, the amount of material, energy & other resources required for steel production should be decreased, along with reduction of usage of steel in products without compromising their quality. JSW Steel has over the years increased the efficiency in the steel making process through augmentation of existing facilities and implementing energy consumption reduction initiatives. JSW also works together with its customers to understand the application of steel in their products and come out with better grades of steel which are well suited to their needs.
- Reuse – It is the use of material or object again either for its original purpose or for a similar purpose, without significantly altering the physical form of the object. JSW contributes to circular economy by reusing the steel-making byproducts in other applications. For e.g. slag is used in cement making, dust is used for extraction of Zinc, hot process gases are used for electricity generation & tar is used for pitch, plastic and fertilizer production
- Re-manufacture – It is the process of restoring durable used steel products to as-new condition to be used for the original application again.
- Recycle – This involves melting of steel products at the end of their useful life to produce new steel. JSW recycles end-of-life steel to produce steel again by replacing hot liquid metal by scrap in the electric arc furnace. Currently, JSW Steel consumes only 4% of scrap and rest all is manufactured by conventional process where iron ore and coal are consumed to make steel. Major challenge was and still persists is the ready availability of end-of-life steel which can be resolved through a national policy in place.
- JSW supports SDG 12: Goal 6 of sustainability information disclosure by regularly disclosing information on its performance of key sustainability parameters along with the sustainable practices adopted in its integrated report which is publicly available on JSW Steel’s website at link
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The Company aims to address the environmental impact of its operations with a strategic and long-term approach. This involves up-gradating and retrofitting infrastructure to make it sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes.
- To achieve this, JSW is continuously evolving to improve raw material quality, energy efficiency, increase steel-making via electric arc furnace process and exploring possibilities in carbon capture and storage/utilization.
- Installation of BF gas holder
- Top-pressure recovery turbine for BF
- Hot stove waste heat recovery
- Installation of energy monitoring and management systems
- Coke oven waste heat recovery boiler
- LD converter dry Gas Cleaning Plant (GCP) and gas holder
- LD convertor waste heat recovery boiler
For more details on all the projects taken up by JSW in the field of resource management please visit the Resource Framework.
SDG3: Good Health & Well Being
- JSW aims to contribute to the Goal 3.9 of SDG 3 whose objective is to substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses caused due to hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination.
- The hazardous chemical used or produced by JSW steel are handled with utmost care ensuring no spillage into soil or water, which thereby causes contamination of the surroundings. Such waste materials are disposed as per the Hazardous Waste Management Rule 2016. The effluent generated is treated and reused inside the plant. All of JSW Steel’s manufacturing locations are Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) i.e. they do not discharge any liquid effluent outside the plant premises and this water post treatment is either recycled in process or used for domestic purposes or horticulture. For more details on how JSW has implemented ZLD please visit the Waste Water Framework.
- JSW regularly monitors the air emissions to ensure they are under the prescribed limit set by Central & State Pollution Control Board (CPCB & SPCB). In addition to that, JSW also implements various air emission management plans to curb and minimize emissions. Some of them include,;
- Dry fog systems installed at 105 junction houses for fugitive emission control
- More than 3 km of wind curtains laid at raw material handling area
- Installation of scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators and bag filters for emission control
Performance of JSW Steel on Climate Change related Parameters
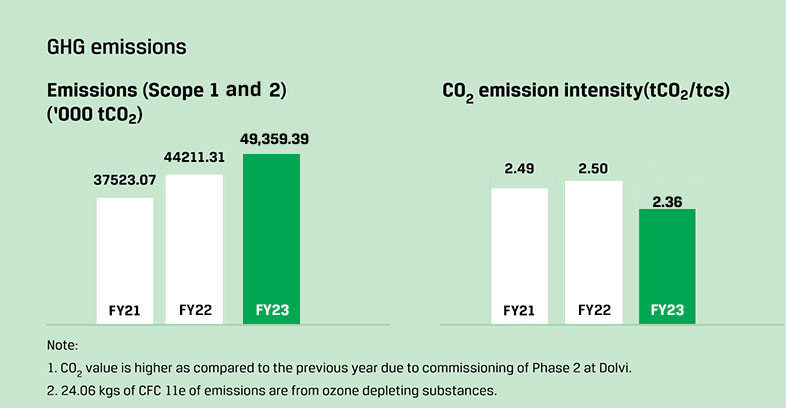
JSW Steel regularly discloses its sustainability performance and initiatives in its integrated report. These reports are available here
